02. Kích thích tố tăng trưởng – Growth Hormone – Song ngữ
English: Tiến sĩ Richard A. Bowen PhD – Professor CSU.
Việt ngữ: Middle Way Group.
Compile: Middle Way Group.
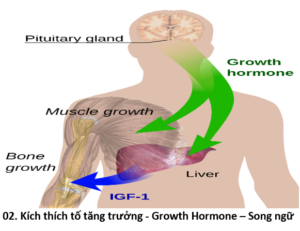
Kích thích tố tăng trưởng – Growth Hormone
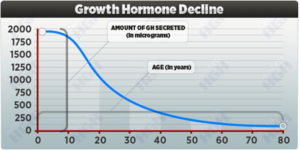
Our bodies secrete growth hormone (GH) at their highest levels during puberty. However, beginning in early adulthood (20s),
GH secretion decreases at an average rate of about 15% per decade.
Cơ thể chúng ta tiết ra hormone tăng trưởng (GH) ở mức cao nhất ở tuổi dậy thì. Tuy nhiên, bắt đầu ở trước tuổi trưởng thành (20 tuổi),
GH tiết giảm với tốc độ trung bình khoảng 15% mỗi mười năm.
**** **** **** ****
Growth hormone is a protein hormone of about 190 amino acids that is synthesized and secreted by cells called somatotrophs in the anterior pituitary. It is a major participant in control of several complex physiologic processes, including growth and metabolism. Growth hormone is also of considerable interest as a drug used in both humans and animals.
Hormone tăng trưởng là một loại protein của khoảng 190 axit amin được tổng hợp và tiết ra bởi các tế bào được gọi là “somatotrophs” trong thùy trước tuyến yên (pituitary gland). Đó là một hormone chính trong sự kiểm soát của một vài quy trình sinh lý phức tạp, bao gồm tăng trưởng và chuyển hóa – của sự trao đổi các phân tử các chất trong cơ thể. Hormone tăng trưởng cũng là mối quan tâm đáng kể như một loại thuốc được sử dụng ở cả người và động vật.
Physiologic Effects of Growth Hormone
Tác dụng sinh lý của Hormone tăng trưởng
A critical concept in understanding growth hormone activity is that it has two distinct types of effects:
Một khái niệm quan trọng trong việc tìm hiểu hoạt động hormone tăng trưởng ở đây là nó có hai loại hiệu ứng riêng biệt:
- Direct effects are the result of growth hormone binding its receptor on target cells. Fat cells (adipocytes), for example, have growth hormone receptors, and growth hormone stimulates them to break down triglyceride and suppresses their ability to take up and accumulate circulating lipids.
Tác động trực tiếp của Hormone tăng trưởng: là liên kết các thụ thể cảm nhận (receptor) của nó trên tế bào mục tiêu. Thí dụ như các tế bào mỡ (adipocytes), có các thụ thể hormone tăng trưởng, và hormone tăng trưởng kích thích chúng để phá vỡ phân tử mở triglyceride và ngăn chặn khả năng hấp thụ của chúng và tích lũy chất béo lưu thông.
- Indirect effects are mediated primarily by a insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I), a hormone that is secreted from the liver and other tissues in response to growth hormone. A majority of the growth promoting effects of growth hormone is actually due to IGF-I acting on its target cells.
Ảnh hưởng gián tiếp qua trung gian chủ yếu: của yếu tố tăng trưởng giống Insulin-1 (IGF – 1), là một hormone được tiết ra từ gan và các mô khác để đáp ứng với hormone tăng trưởng. Một phần lớn của sự tăng trưởng phát huy tác dụng của hormone tăng trưởng thực sự là do “IGF -1” tác động lên các tế bào mục tiêu của nó .
Keeping this distinction in mind, we can discuss two major roles of growth hormone and its minion IGF-I in physiology.
Hãy giữ lấy sự khác biệt này, chúng ta có thể thảo luận về hai vai trò chính của hormone tăng trưởng và tay phụ tá của nó là “IGF –1” trong sinh lý học.
Action of growth hormone
Hành động của Hormone tăng trưởng
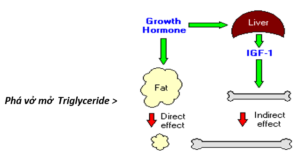
Phá vở mở Triglyceride >
Effects on Growth
Ảnh hưởng trên sự tăng trưởng
Growth is a very complex process, and requires the coordinated action of several hormones. The major role of growth hormone in stimulating body growth is to stimulate the liver and other tissues to secrete IGF-I. IGF-I stimulates proliferation of chondrocytes (cartilage cells), resulting in bone growth. Growth hormone does seem to have a direct effect on bone growth in stimulating differentiation of chondrocytes.
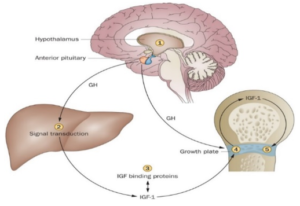
Trưởng thành là một quá trình rất phức tạp, và đòi hỏi sự phối hợp hành động của các loại hormone. Vai trò chủ yếu của hormone tăng trưởng trong việc kích thích tăng trưởng cơ thể, kích thích gan và các mô khác để tiết IGF-1. IGF-1 kích thích sự tăng sinh của tế bào sụn (cartilage cells), dẫn đến sự phát triển xương. Hormone tăng trưởng dường như có tác động trực tiếp đến sự phát triển xương trong việc kích thích sự khác biệt của tế bào sụn.
IGF-1 also appears to be the key player in muscle growth. It stimulates both the differentiation and proliferation of myoblasts. It also stimulates amino acid uptake and protein synthesis in muscle and other tissues.
IGF-1 xuất hiện như là một phần tử quan trọng trong sự tăng trưởng của cơ bắp. Nó kích thích cả hai sự khác biệt và sự gia tăng của các cơ nguyên bào (myoblasts). Nó cũng kích thích sự hấp thu axit amin và tổng hợp protein trong cơ bắp và các mô khác.
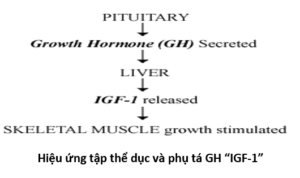
Hiệu ứng tập thể dục và phụ tá GH “IGF-1”
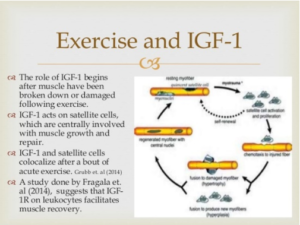
Metabolic Effects
Trao đổi chất hiệu ứng
Growth hormone has important effects on protein, lipid and carbohydrate metabolism. In some cases, a direct effect of growth hormone has been clearly demonstrated, in others, IGF-I is thought to be the critical mediator, and some cases it appears that both direct and indirect effects are at play.
Hormone tăng trưởng có tác dụng quan trọng trên việc chuyển hóa chất đạm (protein), mở (lipid) và đường đơn, đường phức tạp (carbohydrate). Trong một số trường hợp, ảnh hưởng trực tiếp của hormone tăng trưởng đã được chứng minh rõ ràng, ở những người khác, IGF-1 được cho là trung gian quan trọng, và một số trường hợp, nó xuất hiện rằng cả hai tác động trực tiếp và gián tiếp là lúc cơ thể vận động.
Protein metabolism: In general, growth hormone stimulates protein anabolism in many tissues. This effect reflects increased amino acid uptake, increased protein synthesis and decreased oxidation of proteins.
Protein chuyển hóa: Nói chung, hormone tăng trưởng kích thích quá trình đồng hóa protein trong nhiều mô. Hiệu quả này phản ánh sự gia tăng hấp thu axit amin, tăng tổng hợp protein và giảm quá trình oxy hóa của protein.
Fat metabolism: Growth hormone enhances the utilization of fat by stimulating triglyceride breakdown and oxidation in adipocytes.
Chất béo chuyển hóa: hormone tăng trưởng giúp tăng cường việc sử dụng các chất béo bằng cách kích thích sự phá vở mô mở triglyceride và oxy hóa trong tế bào mỡ.
Carbohydrate metabolism: Growth hormone is one of a battery of hormones that serves to maintain blood glucose within a normal range. Growth hormone is often said to have anti-insulin activity, because it suppresses the abilities of insulin to stimulate uptake of glucose in peripheral tissues and enhance glucose synthesis in the liver. Somewhat paradoxically, administration of growth hormone stimulates insulin secretion, leading to hyperinsulinemia.
Chuyển hóa Carbohydrate: Hóc môn tăng trưởng là một bình điện cho các hormone khác, nó nhiệm vụ duy trì đường huyết trong một phạm vi bình thường. Hormone tăng trưởng thường được cho là có hoạt tính kháng insulin, bởi vì nó ngăn chặn khả năng của insulin để kích thích sự hấp thu glucose ở các mô ngoại vi và tăng cường tổng hợp glucose ở gan. Có vẻ nghịch lý, sự điều hành của hormone tăng trưởng là kích thích bài tiết insulin, dẫn tới tăng insulin. Trong khi nó thường được nhầm lẫn với bệnh tiểu đường hoặc tăng đường huyết.
Control of Growth Hormone Secretion
Kiểm soát sự sản xuất của hormone tăng trưởng
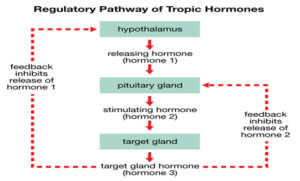
Production of growth hormone is modulated by many factors, including stress, exercise, nutrition, sleep and growth hormone itself. However, its primary controllers are two hypothalamic hormones and one hormone from the stomach:
Sự sản xuất hormone tăng trưởng được điều chỉnh bởi nhiều yếu tố, bao gồm stress, tập thể dục, dinh dưỡng, giấc ngủ và hormone tăng trưởng của chính nó. Tuy nhiên, bộ điều khiển chính của nó là hai hormon vùng dưới đồi và một hormone từ dạ dày:
Growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH) is a hypothalamic peptide that stimulates both the synthesis and secretion of growth hormone.
Tăng trưởng hormone hormone-releasing (GHRH) là một loại chất đạm cơ bản (peptide) ở vùng dưới đồi kích thích cả hai sự tổng hợp và tiết ra hormone tăng trưởng.
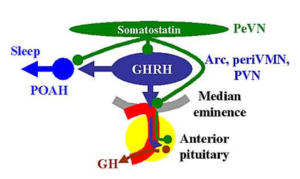
Somatostatin (SS) is a peptide produced by several tissues in the body, including the hypothalamus. Somatostatin inhibits growth hormone release in response to GHRH and to other stimulatory factors such as low blood glucose concentration.
Somatostatin (SS) là một loại chất đạm cơ bản (peptide) được sản xuất bởi một số các mô trong cơ thể, bao gồm cả vùng dưới đồi. Somatostatin ức chế sự tăng trưởng phát hành hormone để đáp ứng với GHRH và các yếu tố kích thích khác như nồng độ glucose trong máu thấp.
Ghrelin is a peptide hormone secreted from the stomach. Ghrelin binds to receptors on somatotrophs and potently stimulates secretion of growth hormone.
Ghrelin là một loại chất đạm cơ bản (peptide) được tiết ra từ dạ dày. Ghrelin gắn với thụ thể cảm nhận trên somatotrophs và có khả năng kích thích bài tiết hormone tăng trưởng.
Growth hormone secretion is also part of a negative feedback loop involving IGF-I. High blood levels of IGF-I lead to decreased secretion of growth hormone not only by directly suppressing the somatotroph, but by stimulating release of somatostatin from the hypothalamus.
Growth hormone also feeds back to inhibit GHRH secretion and probably has a direct (autocrine) inhibitory effect on secretion from the somatotroph.
Sự tiết ra hormone tăng trưởng cũng là một phần của một vòng phản hồi tiêu cực liên quan đến IGF-I. Nồng độ trong máu cao của IGF-I dẫn đến giảm tiết ra hormone tăng trưởng không chỉ bằng cách trực tiếp đàn áp tế bào somatotroph, nhưng bằng cách kích thích phát hành của somatostatin từ vùng dưới đồi.
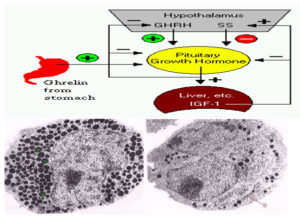
“Above are two electron micrographs of the typical
appearance of isolated cultured somatotrophs before and after.”
“Trên đây là hình của hai tế bào somatotrophs nuôi cách ly trước và sau – được chụp từ kiến hiển vi electron.”
Hormone tăng trưởng còn phản ứng lại để ức chế sự tiết ra GHRH và có thể có một (autocrine) tác dụng ức chế trực tiếp trên sự tiết ra từ tế bào somatotroph.
Integration of all the factors that affect growth hormone synthesis and secretion lead to a pulsatile pattern of release. Basal concentrations of growth hormone in blood are very low. In children and young adults, the most intense period of growth hormone release is shortly after the onset of deep sleep.
Phân tích tổng hợp tất cả các yếu tố ảnh hưởng đến tốc độ tổng hợp hormone tăng trưởng và sự tiết ra của nó, dẫn đến một mô hình đồng bộ phóng thích ra GH. Nồng độ cơ bản của GH trong máu là rất thấp. Ở trẻ em và người trẻ tuổi trung niên, giai đoạn căng thẳng nhất của sự tiết ra GH là ngay sau khi sự khởi đầu của giấc ngủ sâu.
Disease States of Growth Hormone
Tình trạng bịnh tật của Hormone tăng trưởng
States of both growth hormone deficiency and excess provide very visible testaments to the role of this hormone in normal physiology. Such disorders can reflect lesions in either the hypothalamus, the pituitary or in target cells. A deficiency state can result not only from a deficiency in production of the hormone, but in the target cell’s response to the hormone.
Tình trạng của cả hai thiếu và dư thừa GH cung cấp một chứng cớ rất rõ ràng về vai trò của GH này trong sinh lý bình thường. Rối loạn thiếu và thừa này có thể phản ánh những tổn thương trong vùng dưới đồi, tuyến yên hoặc trong các tế bào mục tiêu. Một trạng thái thiếu hụt có thể dẫn đến – không chỉ từ sự thiếu hụt trong sản xuất của các hormone, mà còn sự phản ứng của các tế bào mục tiêu đến nội tiết tố GH.
Clinically, deficiency in growth hormone or defects in its binding to receptor are seen as growth retardation or dwarfism. The manifestation of growth hormone deficiency depends upon the age of onset of the disorder and can result from either heritable or acquired disease.
Trên phương diện lâm sàng, sự thiếu hụt GH hoặc các khuyết tật của nó khi liên kết với thụ thể cảm nhận (receptor) được coi là chậm phát triển hoặc là còi cọc. Các biểu hiện của sự thiếu GH phụ thuộc vào tuổi phát bệnh của các sự rối loạn và cũng có thể là kết quả của một trong hai – một là bệnh di truyền hoặc thứ hai là tự bị mắc phải.
The effect of excessive secretion of growth hormone is also very dependent on the age of onset and is seen as two distinctive disorders:
Hiệu quả của sự tiết quá nhiều GH cũng là rất phụ thuộc vào tuổi phát bệnh và được coi là có hai rối loạn đặc biệt:
Giantism is the result of excessive growth hormone secretion that begins in young children or adolescents. It is a very rare disorder, usually resulting from a tumor of somatotropes. One of the most famous giants was a man named Robert Wadlow. He weighed 8.5 pounds at birth, but by 5 years of age was 105 pounds and 5 feet 4 inches tall. Robert reached an adult weight of 490 pounds and 8 feet 11 inches in height. He died at age 22.
Sự to lớn dị thường là kết quả của sự tiết ra GH quá mức mà bắt đầu ở trẻ em hoặc thanh thiếu niên. Đây là một rối loạn rất hiếm gặp, thường là kết quả từ một khối u của tế bào tiết ra GH (somatotropes). Một trong những sự to lớn dị thường nổi tiếng nhất là một người đàn ông tên là Robert Wadlow. Ông ta nặng 8.5 lbs khi sinh, nhưng 5 tuổi là 105 lbs và cao 5 feet 4 inches. Robert đã đạt được một trọng lượng của người lớn là 490 lbs và 8 feet 11 inches chiều cao. Ông qua đời ở tuổi 22.
Acromegaly results from excessive secretion of growth hormone in adults, usually the result of benign pituitary tumors. The onset of this disorder is typically insidious, occurring over several years. Clinical signs of acromegaly include overgrowth of extremities, soft-tissue swelling, abnormalities in jaw structure and cardiac disease. The excessive growth hormone and IGF-I also lead to a number of metabolic derangements, including hyperglycemia.
Bệnh to cực là kết quả từ sự tiết ra quá nhiều GH ở người lớn, thường là kết quả của các khối u lành ở tuyến yên. Sự khởi đầu của rối loạn này thường xảy ra âm thầm, xảy ra trong nhiều năm. Triệu chứng lâm sàng của Bệnh to cực bao gồm phát triển quá mức của tứ chi, sưng mô mềm, những bất thường trong cấu trúc xương hàm và bệnh tim. Sự dư thừa quá mức của GH và IGF-1 cũng dẫn đến một số số rối loạn chuyển hóa, bao gồm tăng đường trong máu.
Pharmaceutical and Biotechnological Uses of Growth Hormone
Dược phẩm và Công nghệ Sinh Dùng Hormone tăng trưởng GH
In years past, growth hormone purified from human cadaver pituitaries was used to treat children with severe growth retardation. More recently, the virtually unlimited supply of growth hormone produced using recombinant DNA technology has led to several other applications to human and animal populations.
Trong những năm qua, GH đã được tinh chế từ các “Tuyến Yên” của tử thi con người đã được sử dụng để điều trị trẻ em bị chậm phát triển nghiêm trọng. Gần đây, việc cung cấp hầu như không giới hạn của hormone tăng trưởng GH được sản xuất – do sử dụng công nghệ DNA tái tổ hợp – đã dẫn đến một số ứng dụng khác để quần thể người và động vật.
Human growth hormone is commonly used to treat children of pathologically short stature. There is concern that this practice will be extended to treatment of essentially normal children – so called “enhancement therapy” or growth hormone on demand. Similarly, growth hormone has been used by some to enhance athletic performance. Although growth hormone therapy is generally safe, it is not as safe as no therapy and does entail unpredictable health risks. Parents that request growth hormone therapy for children of essentially-normal stature are clearly misguided.
Hormone tăng trưởng GH của con người thì thường được sử dụng để điều trị trẻ em bị bịnh có tầm vóc ngắn. Có sự quan tâm rằng, sự thực hành này sẽ được mở rộng để điều trị trẻ em cơ bản bình thường – vì vậy được gọi là “liệu pháp mở rộng” hay hormone tăng trưởng về nhu cầu. Tương tự như vậy, hormone tăng trưởng đã được sử dụng bởi một số để nâng cao hiệu suất thể thao. Mặc dù liệu pháp hormone tăng trưởng nói chung là an toàn, nó không phải là an toàn như không có điều trị và không kéo theo nguy cơ sức khỏe không thể đoán trước. Cha mẹ có yêu cầu điều trị hormone tăng trưởng cho trẻ tầm vóc cơ bản bình thường rõ ràng là sai lầm.
The role of growth hormone in normal aging remains poorly understood, but some of the cosmetic symptoms of aging appear to be amenable to growth hormone therapy. This is an active area of research, and additional information and recommendations about risks and benefits will undoubtedly surface in the near future.
Vai trò của các hormone tăng trưởng GH trong quá trình lão hóa bình thường vẫn chưa được hiểu rõ, nhưng một số triệu chứng của lão hóa mỹ phẩm xuất hiện để thể thích hợp với liệu pháp hormone tăng trưởng. Đây là một lĩnh vực mới trong nghiên cứu, và bổ sung thông tin và kiến nghị về những rủi ro và lợi ích chắc chắn sẽ xuất hiện trong tương lai gần.
Growth hormone is currently approved and marketed for enhancing milk production in dairy cattle. There is no doubt that administration of bovine somatotropin to lactating cow’s results in increased milk yield, and, depending on the way the cows are managed, can be an economically-viable therapy. However, this treatment engenders abundant controversy, even among dairy farmers. One thing that appears clear is that drinking milk from cattle treated with bovine growth hormone does not pose a risk to human health.
Hormone tăng trưởng GH hiện nay được chấp nhận và tiếp thị để tăng cường sản xuất sữa ở bò sữa. Không có nghi ngờ rằng cho bò sửa ăn loại Hormone chuyển thể – mục đích cho bò sản xuật sửa nhiều hơn – để tăng sản lượng sữa nhiều hơn, và, tùy thuộc vào cách những con bò được quản lý, có thể là một liệu pháp kinh tế khả thi. Tuy nhiên, điều trị này sanh ra tranh cãi dồi dào, thậm chí giữa các nông dân chăn nuôi bò sữa. Một điều mà dường như rõ ràng là uống sữa từ gia súc được điều trị bằng hormone tăng trưởng ở bò không gây nguy hiểm cho sức khỏe con người.
Another application of growth hormone in animal agriculture is treatment of growing pigs with porcine growth hormone. Such treatment has been demonstrated to significantly stimulate muscle growth and reduce deposition of fat.
Một ứng dụng khác của hormone tăng trưởng GH trong nông nghiệp chăn nuôi là điều trị lợn thịt với hormone tăng trưởng của heo. Điều trị như đã được chứng minh để kích thích đáng kể tăng trưởng cơ bắp thịt nạc và giảm tích tụ chất béo.

Growth hormone (GH) helps control protein, fat and carbohydrate metabolism in adults at rest and during exercise. A review of literature from the University of Virginia, led by Art Weltman, concluded that growth hormone release increased with the intensity of exercise.
Hormone tăng trưởng (GH) giúp kiểm soát protein, chất béo và chuyển hóa carbohydrate ở người lớn khi nghĩ ngơi và trong khi tập luyện.
Một đánh giá từ Đại học Virginia, dẫn đầu bởi Art Weltman,
kết luận rằng GH tăng với cường độ tập thể dục
Sources:
Tài liệu tham khảo:
- http://arbl.cvmbs.colostate.edu/hbooks/pathphys/endocrine/hypopit/gh.html
- http://tusach.thuvienkhoahoc.com/
- https://www.google.com/search?q=gh+and+age+images
- http://fitnessrxformen.com/training/growth-hormone/
